Attendees to this meetup, will go through the process of creating an example EVP for their organization. Creating EVPs is a process that should be as collaborative as possible, involving staff across all demographics. Organizations should also create multiple EVPs (or multiple variations) to cater for the fact that each person is motivated differently. The EVP created during the meetup will show how – with the expectation that attendees can then create something similar with their organizations.
Preparation | Room Setup | Facilitation Process | Post-Event Mailout
Preparation
Optionally, we recommend getting sufficient copies of the “Employee Engagement – a Strategic Differentiator in Today’s Competitive Business Landscape” report printed for the attendees. If you have a sponsor, full colour on good paper is best. However, this can also be done in a cost-effective way.
You should also send out copies of the reports to all registered attendees prior to the meetup.
People will be working in groups of 5-9. Ensure sufficient flips charts (or whiteboards or large-format adhesive sheets) as your have groups are available. Each group should also have 2-3 post-it note pads and sharpies.
Room Setup
Place as many flip charts around the room as you expect groups. Set up some chairs around the room for people to use if they get tired of standing, but expect that most people will be standing and working most of the time.
Facilitation Process
Start by introducing the concepts from the Report. I do not recommend slides, although you are welcome to use them if needed. Talk through the main points to convey what the importance of employee engagement – emphasising the fact that agile organisations have higher engagement scores than non-agile organisations.
Setting Context & Demographics
Ask each group to select one of their constituent organisations to use as the example case. Get that person to briefly describe their company, the kind of people who work there, and the culture of the organisation. As they discuss, ask them to add post-it notes to the first sheet with key points about the workforce (e.g. full-time or contingent workers, collocated or remote, various nationalities represented, different generations and so on).
Empathy maps
Then ask each group to draw an empathy map on the second sheet. An empathy map is a chart that helps you understand someone else. You fill it out in order to get a sense of how things look from where they’re sitting – what they experience; how they feel; what they think, say and do – in short, to empathize with them. How do you find out what to put down in the chart? Ask them all to brainstorm fill in 4 quadrants;
What does s/he THINK & FEEL?
|
What does s/he HEAR?
|
What does s/he SEE?
|
What does s/he SAY AND DO?
|
10 most important drivers for engagement
Next, ask the group to brainstorm the potential drivers for employee engagement. Please note that the report has example drivers that can be referred to. These are cultural behaviours and workplace practices that help to develop a sense of purpose and engagement. These may relate to;
-
- Communication and Interactions
- Organisational Purpose
- Personal/Individual
- Logistics and Administration
- Psychological Safety
- Inclusivity
- Rewards and Remuneration
Ask the group to identify what they think are the 10 most important drivers.
Kano Model
Next, ask the group to draw up a Kano chart on the next chart. Something similar to this.
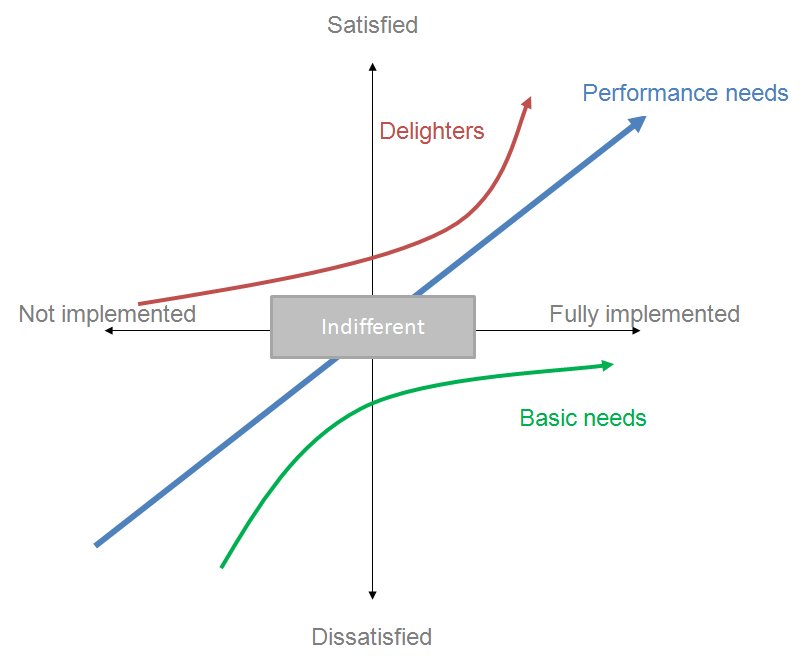
Explain that drivers fall into four general types:
- Linear drivers (Performers) contribute to higher and higher employee engagement the more they’re present, with engagement dropping proportionally the less the driver is evident.
- Hygiene drivers, or “must-haves” (Basic), support engagement up to a certain level, after which improving on them doesn’t significantly impact engagement (e.g., salary and benefits).
- Delighters are drivers that have no major negative impact if they’re missing, but which can have an important positive impact if fulfilled.
- Reverse drivers make employees less engaged the more they’re in evidence.
Ask the team to put each driver (on a post-it note) on the Kano model where they think it belongs (Performer, Basic, or Delighter).
Designing a Programme
If there is time (depending on how long the meetup is), you can then brainstorm the way forward. Get the team to design a programme to implement a few of the drivers – including at least one delighter.
At the end, ask each group to present their EVP to the audience.
Post-Event Mailout
Send out any photos from the event and invite them to join the HR Guild and Business Agility Institute.
